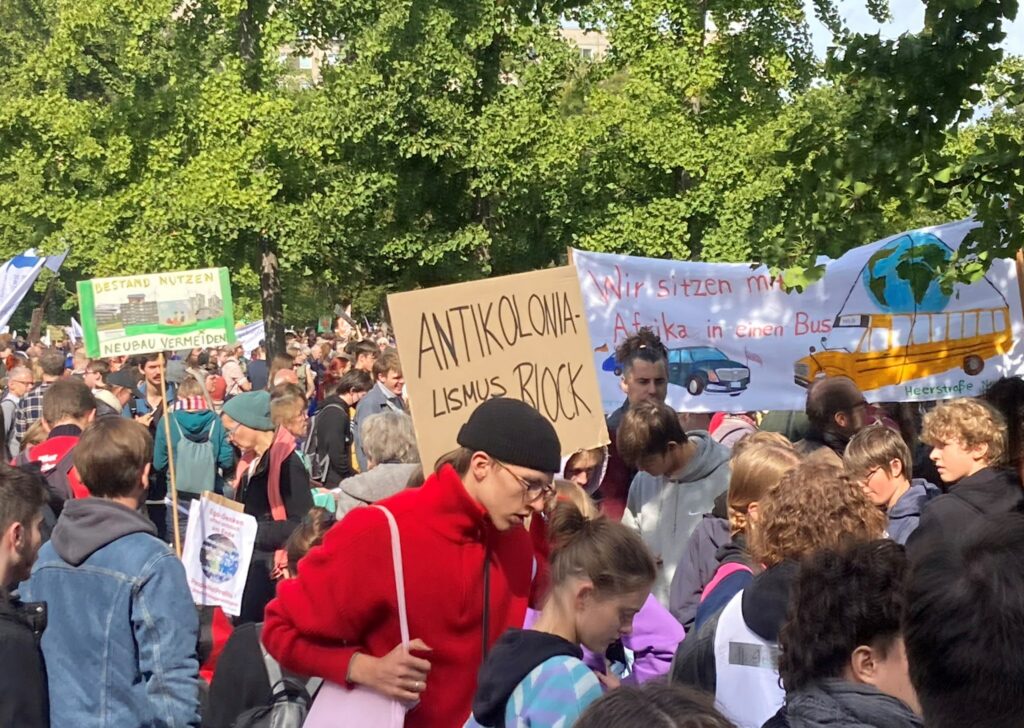
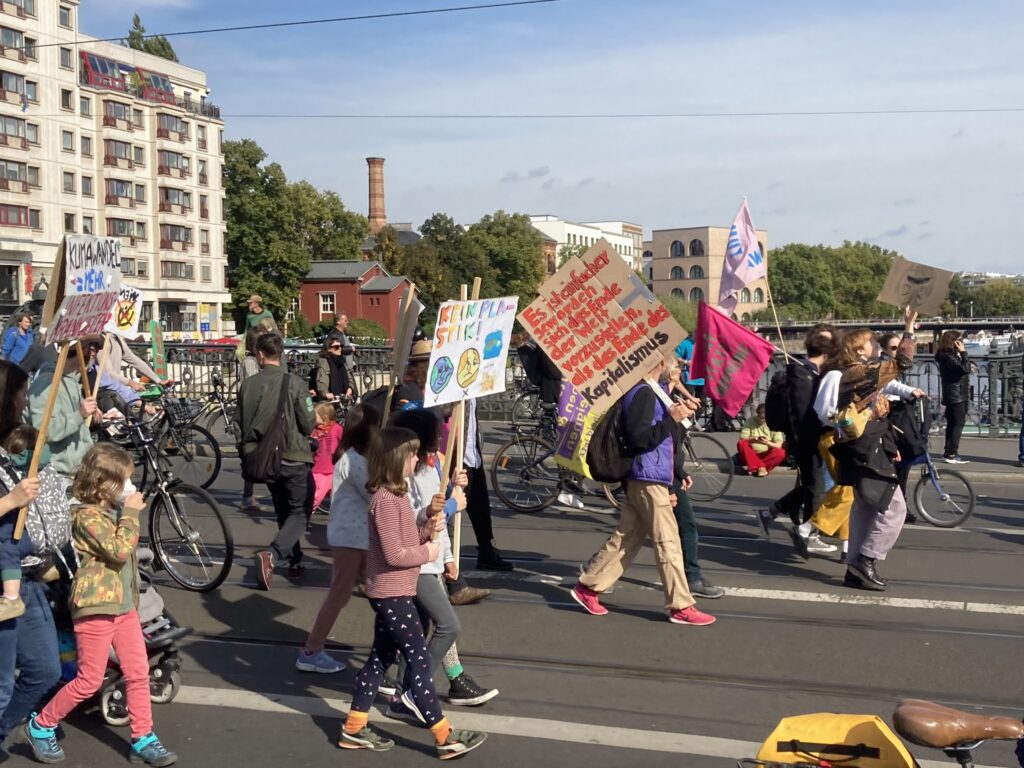
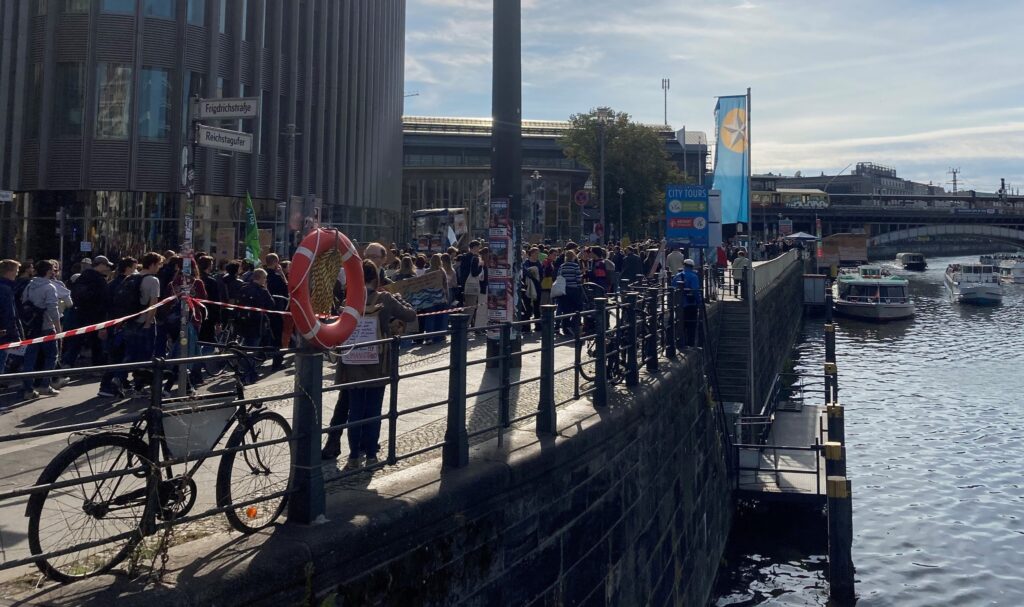
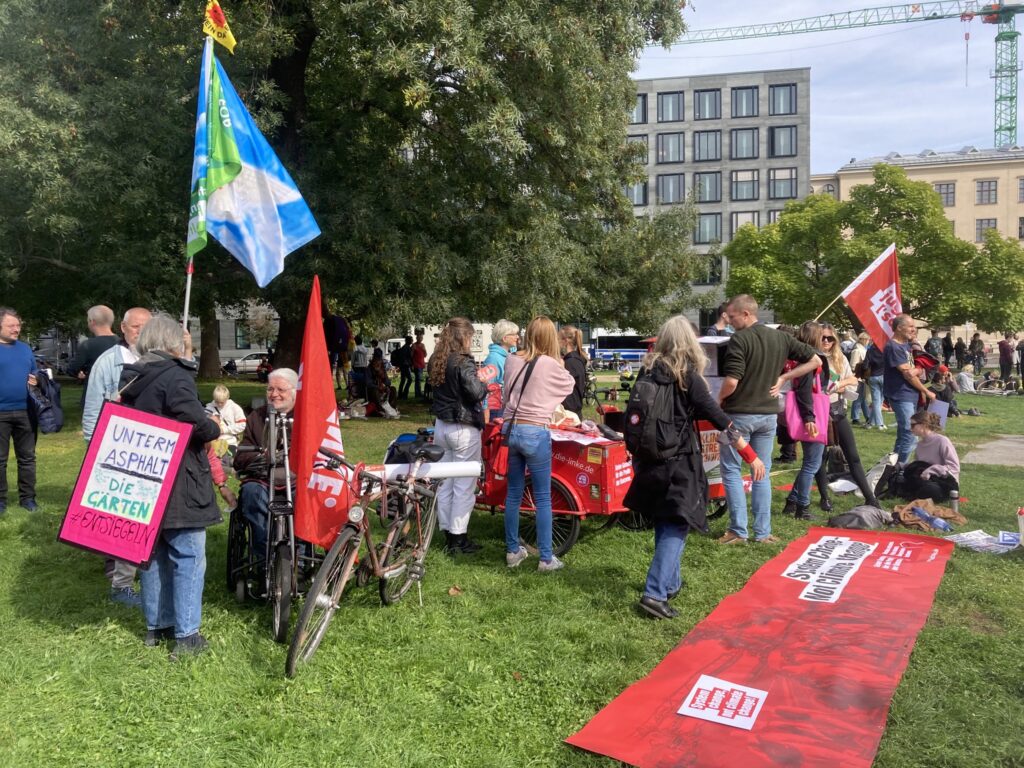
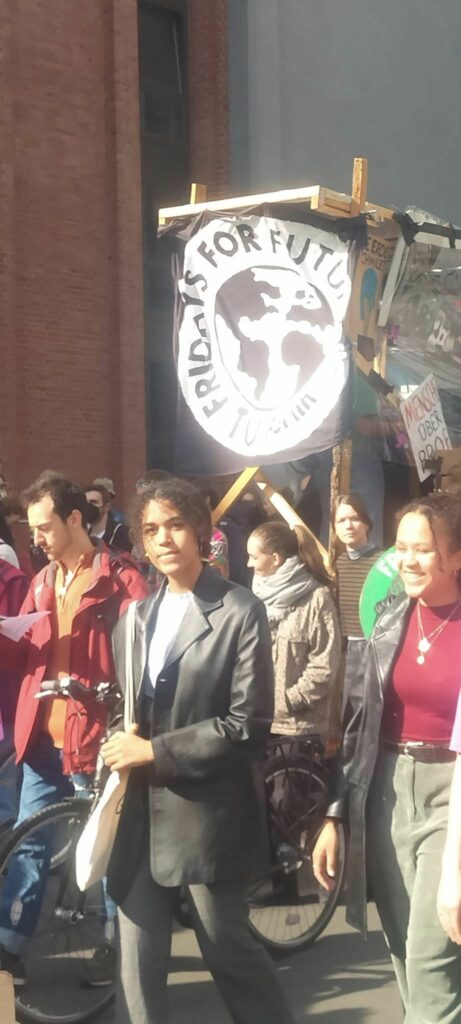
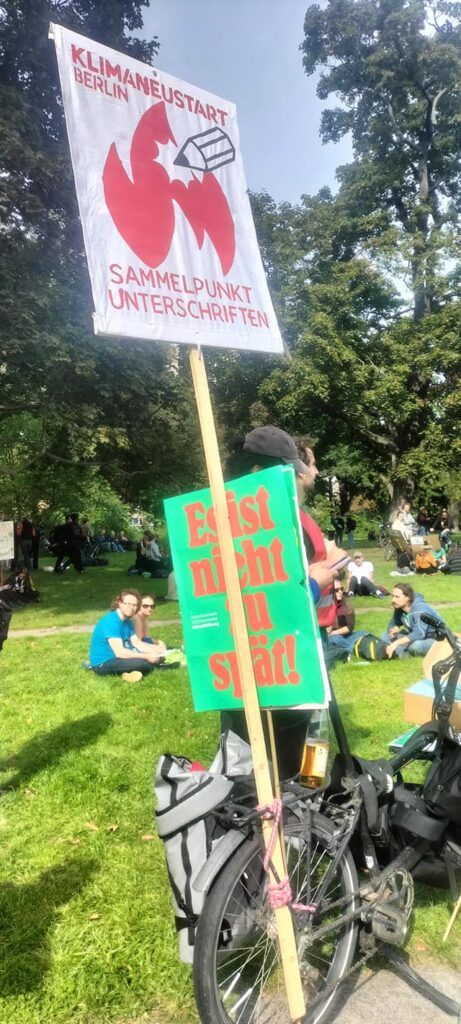
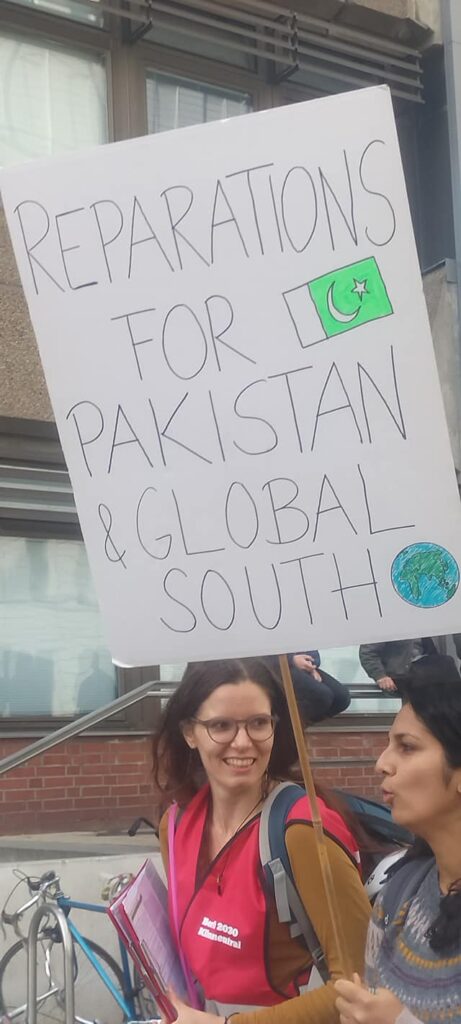
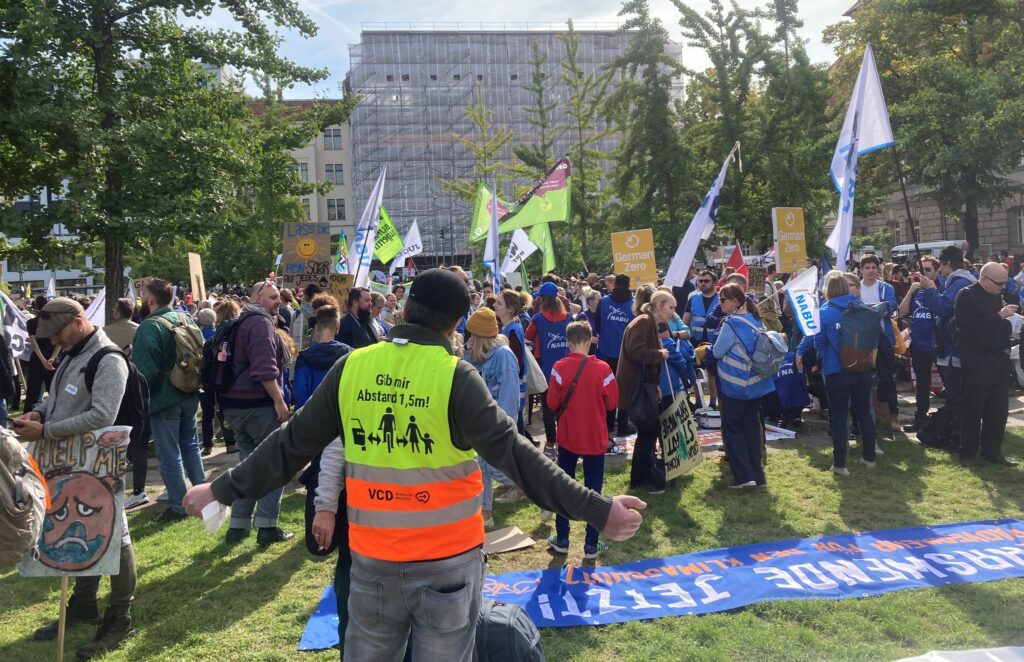
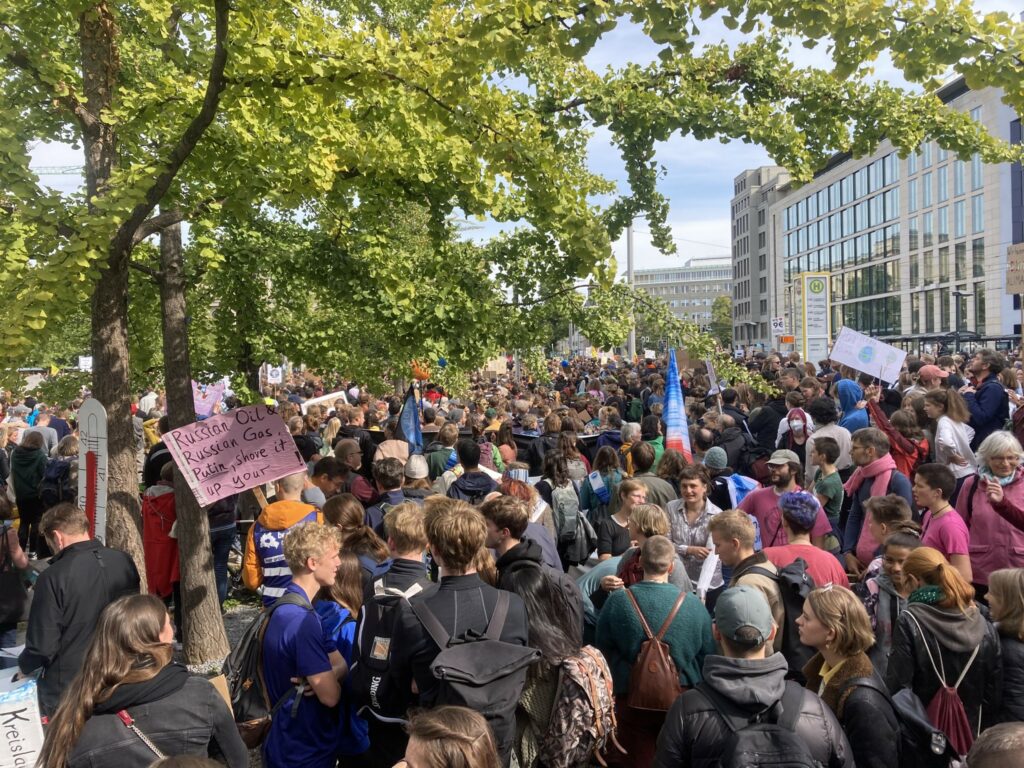
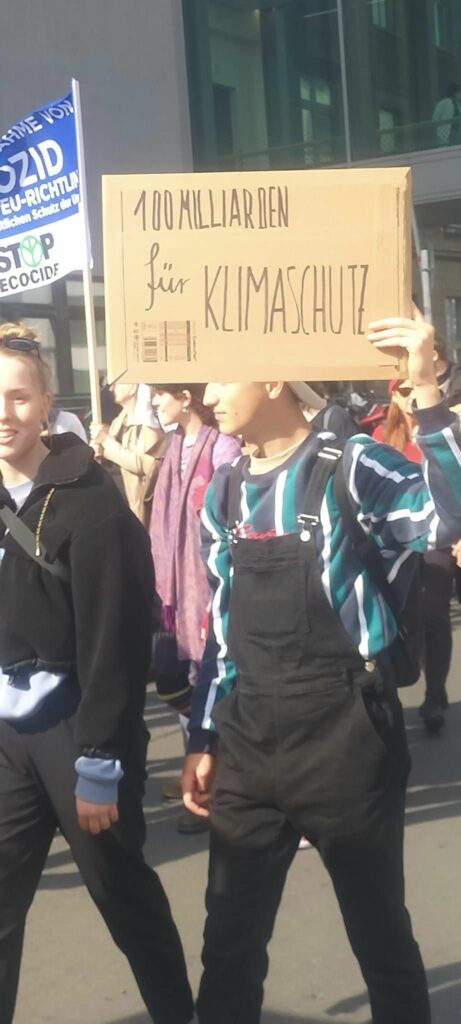
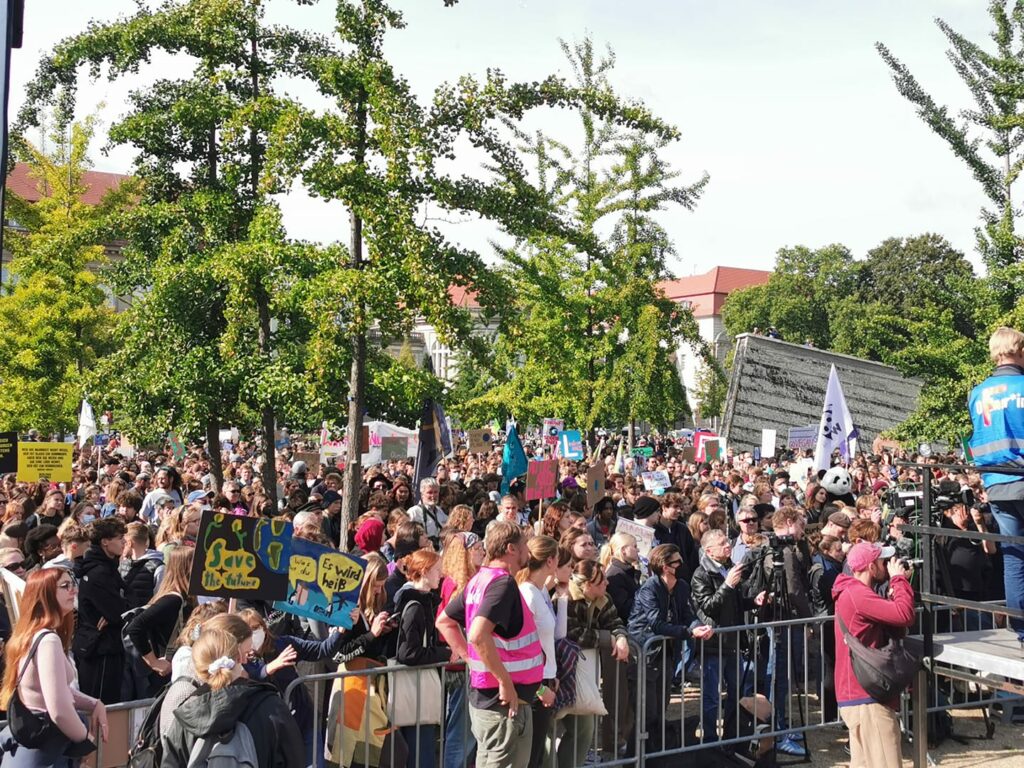
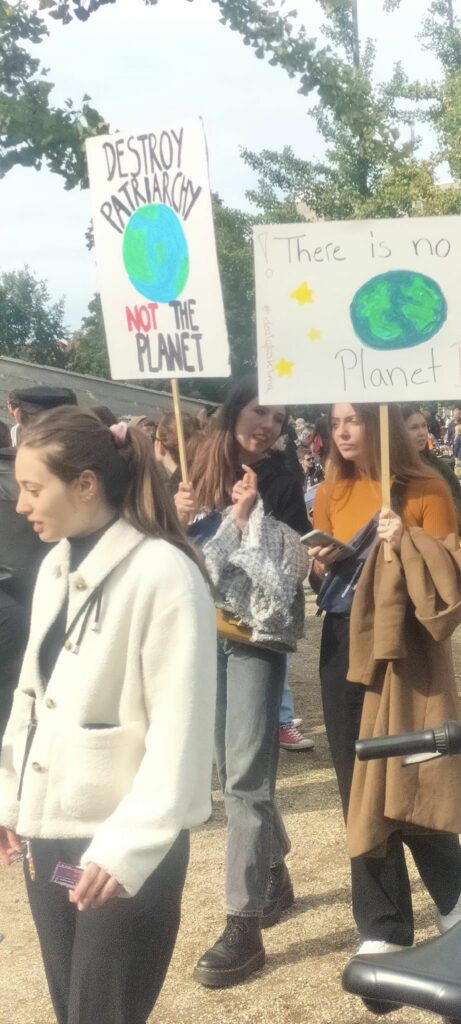
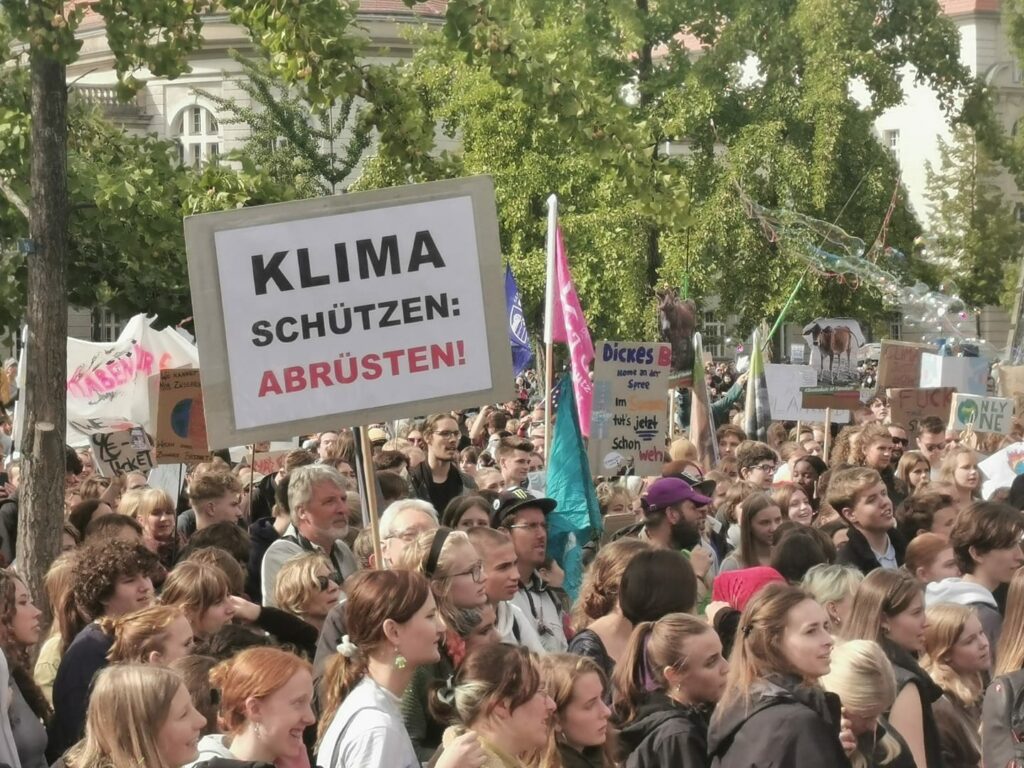
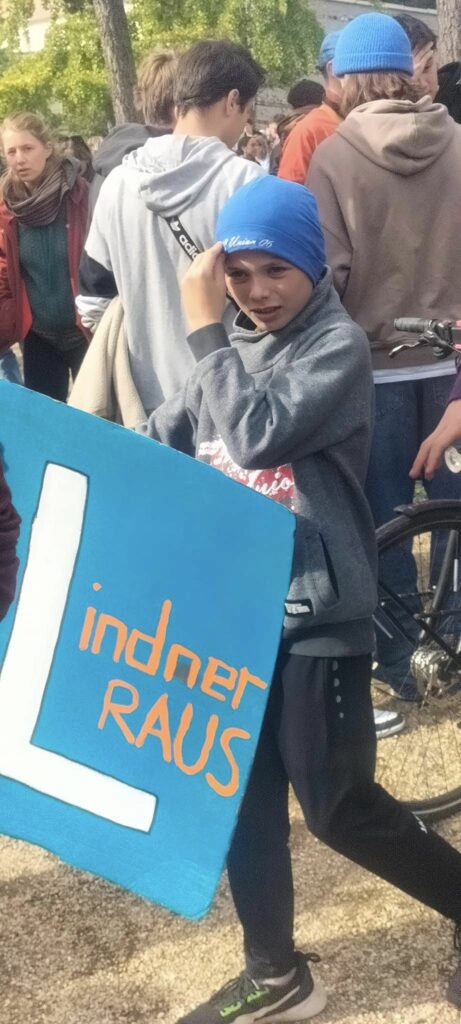
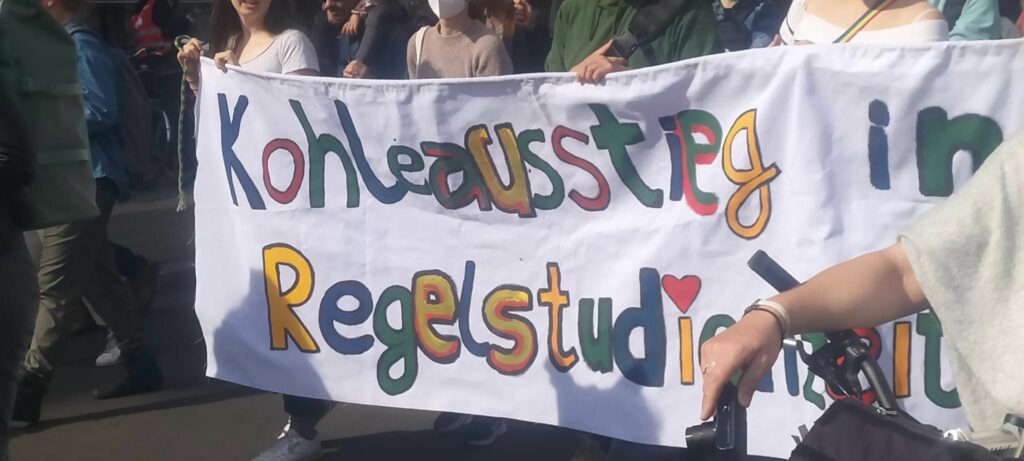
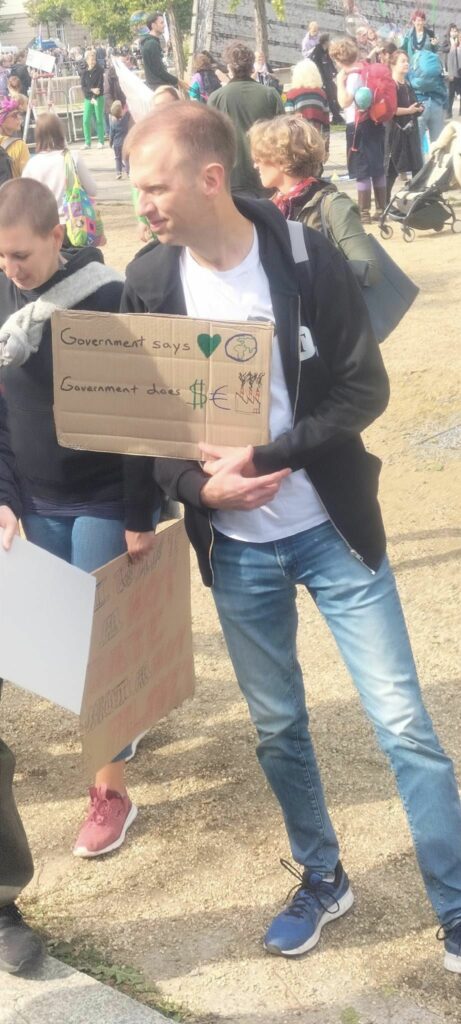
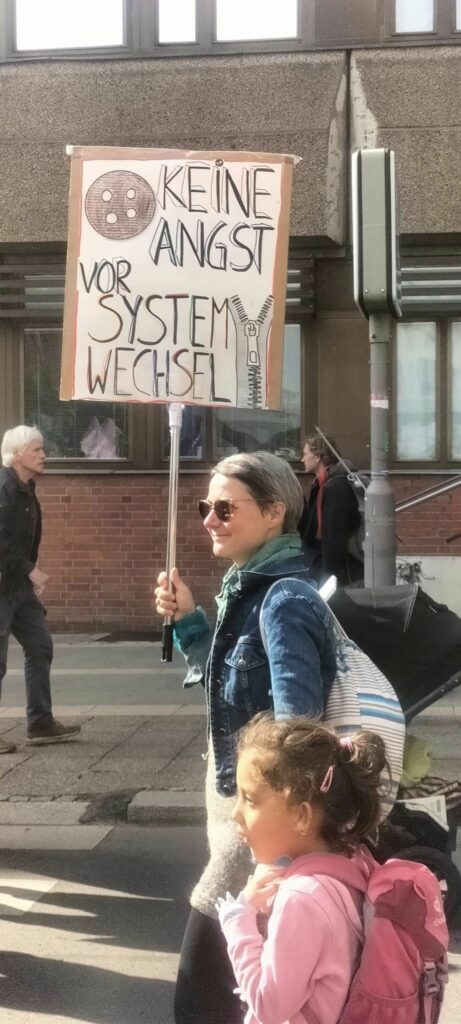
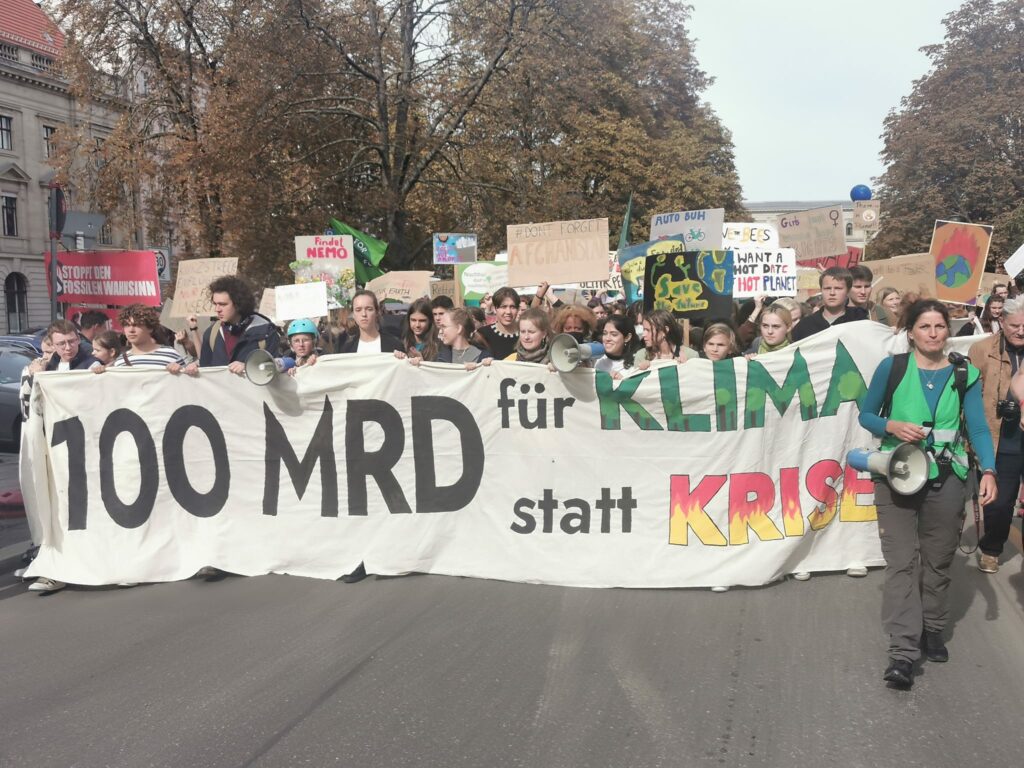
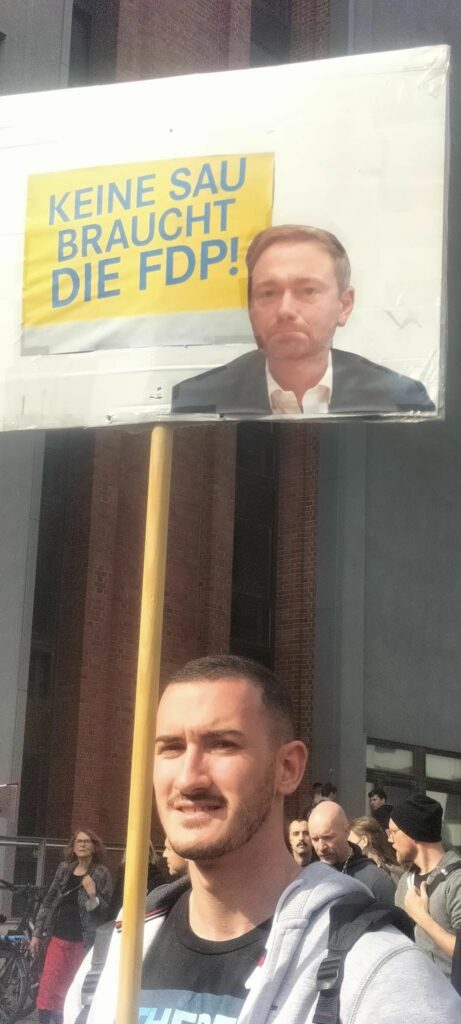
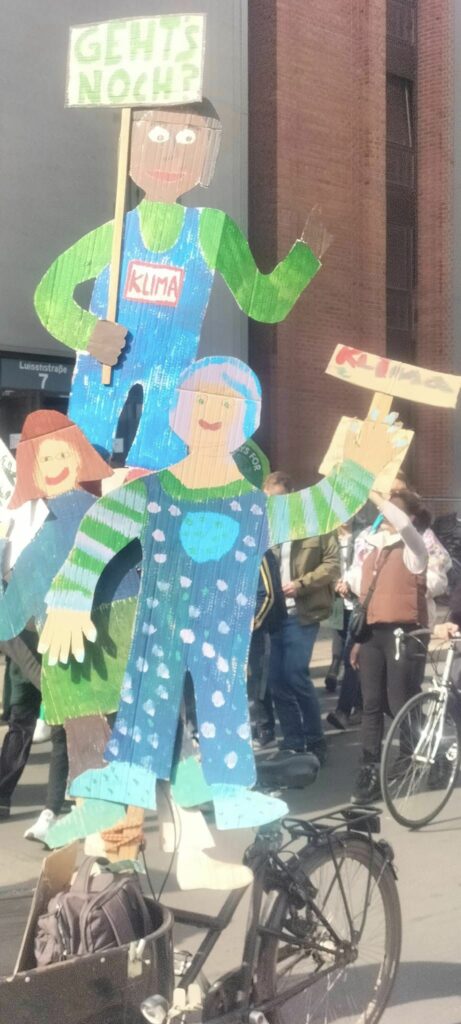
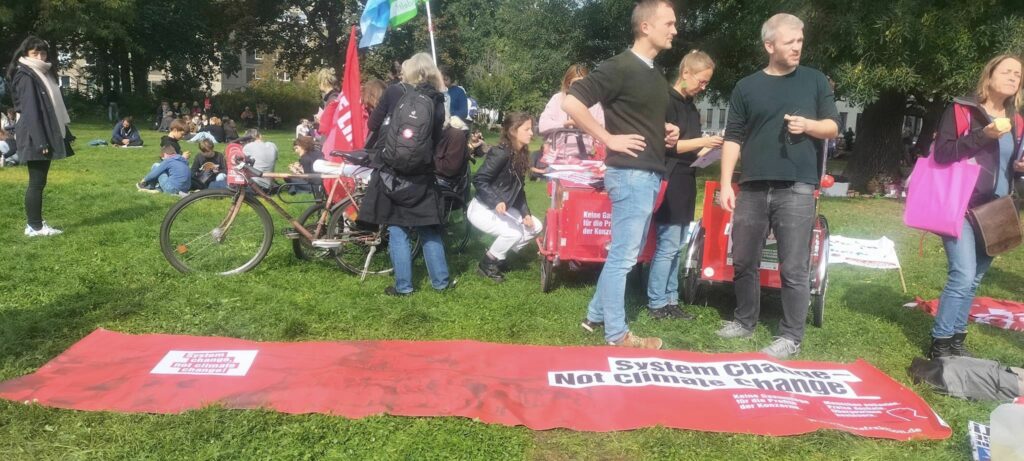
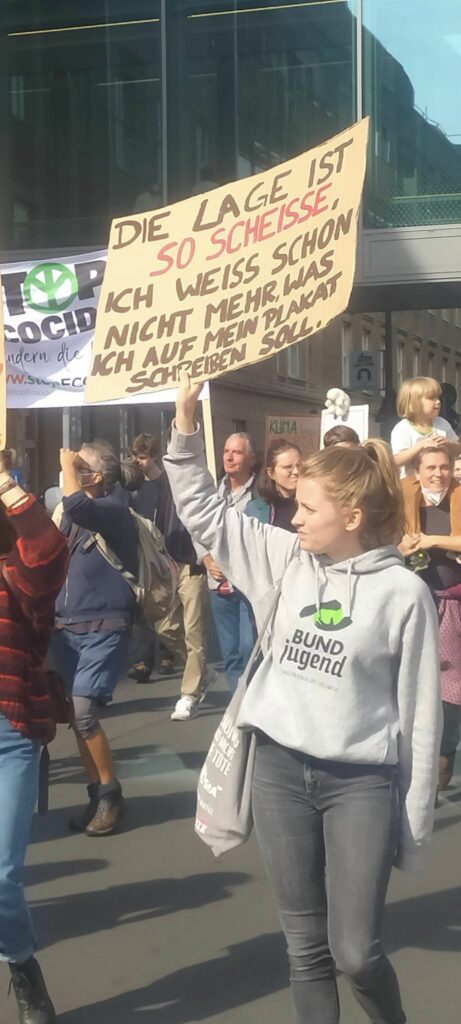
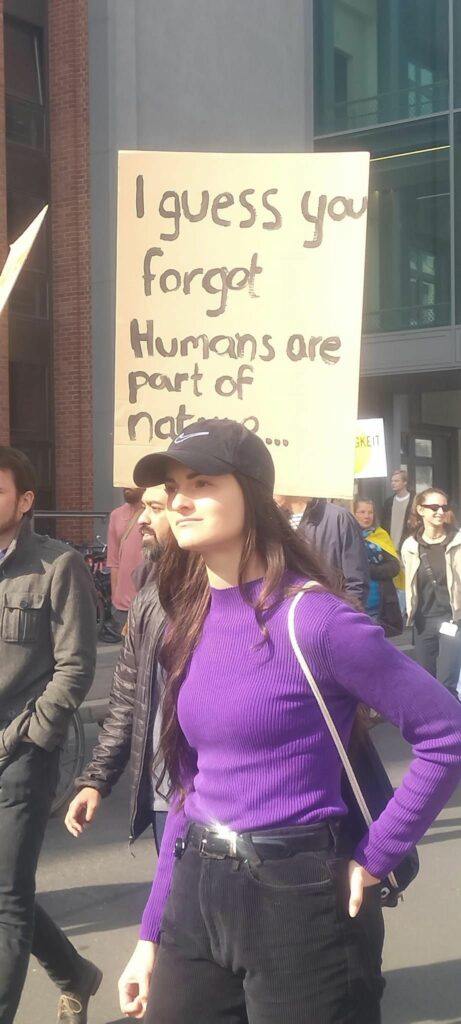
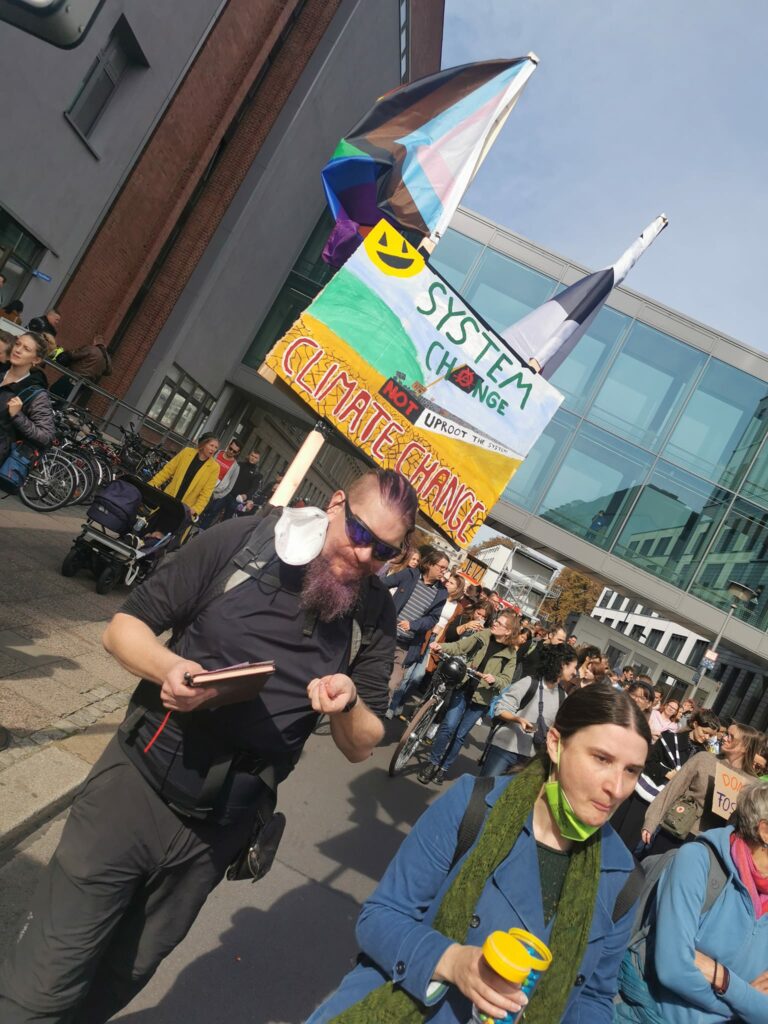
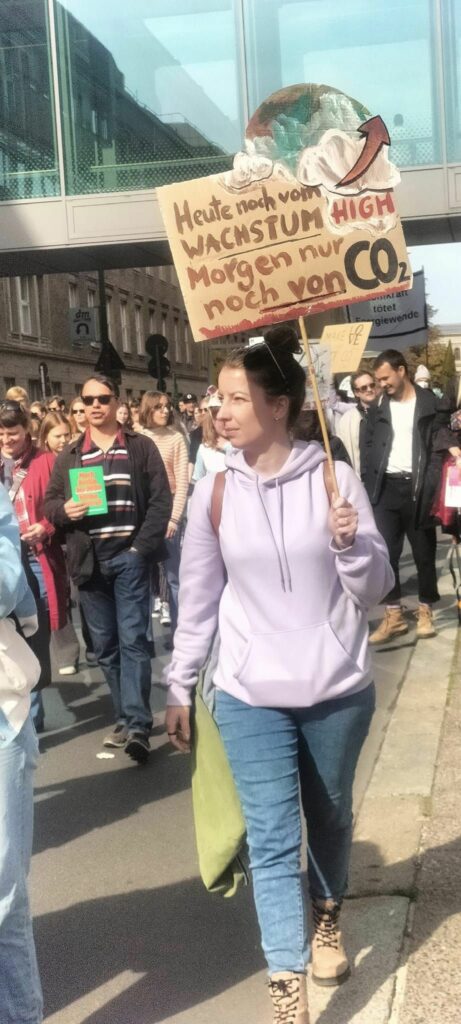
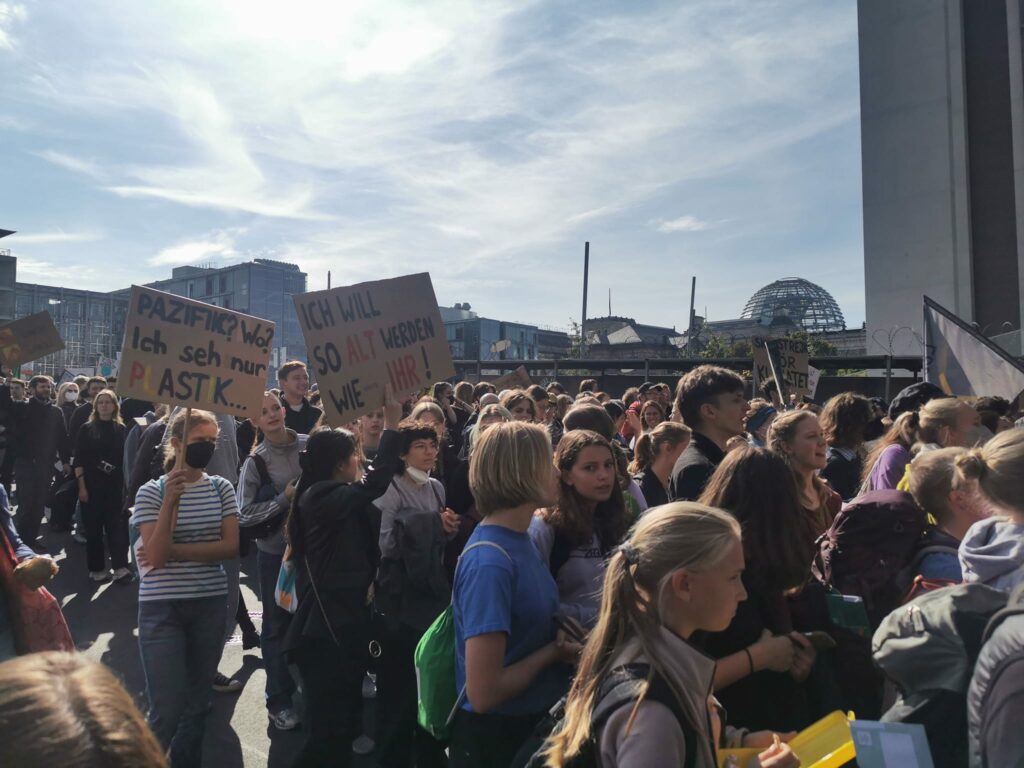
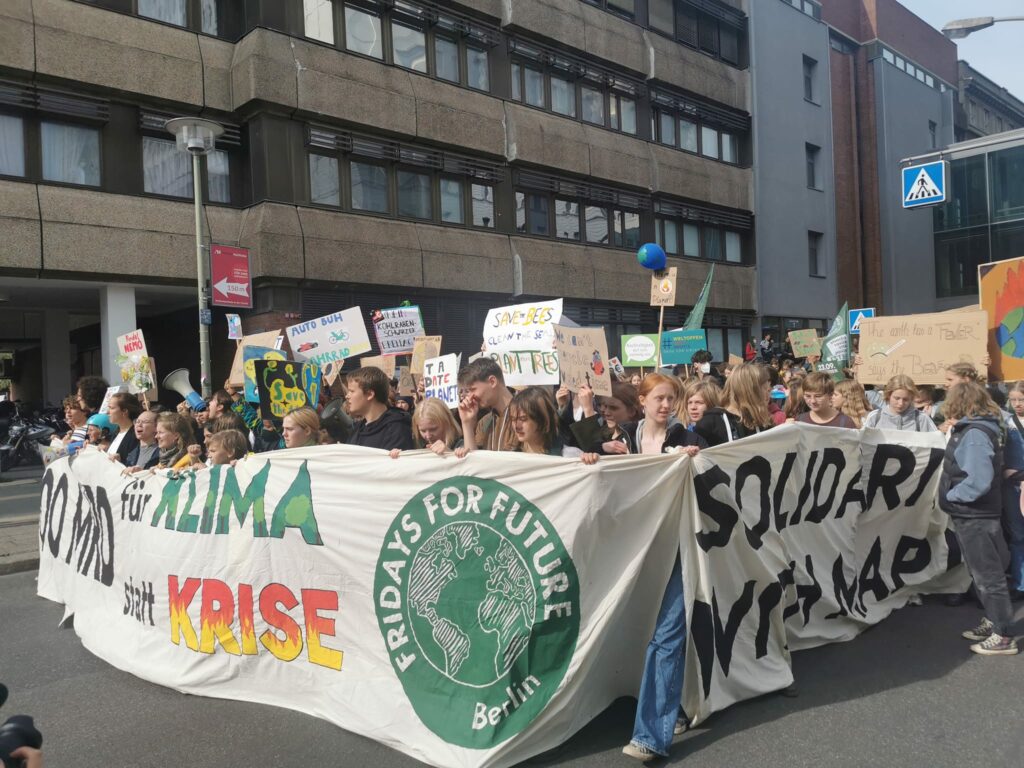
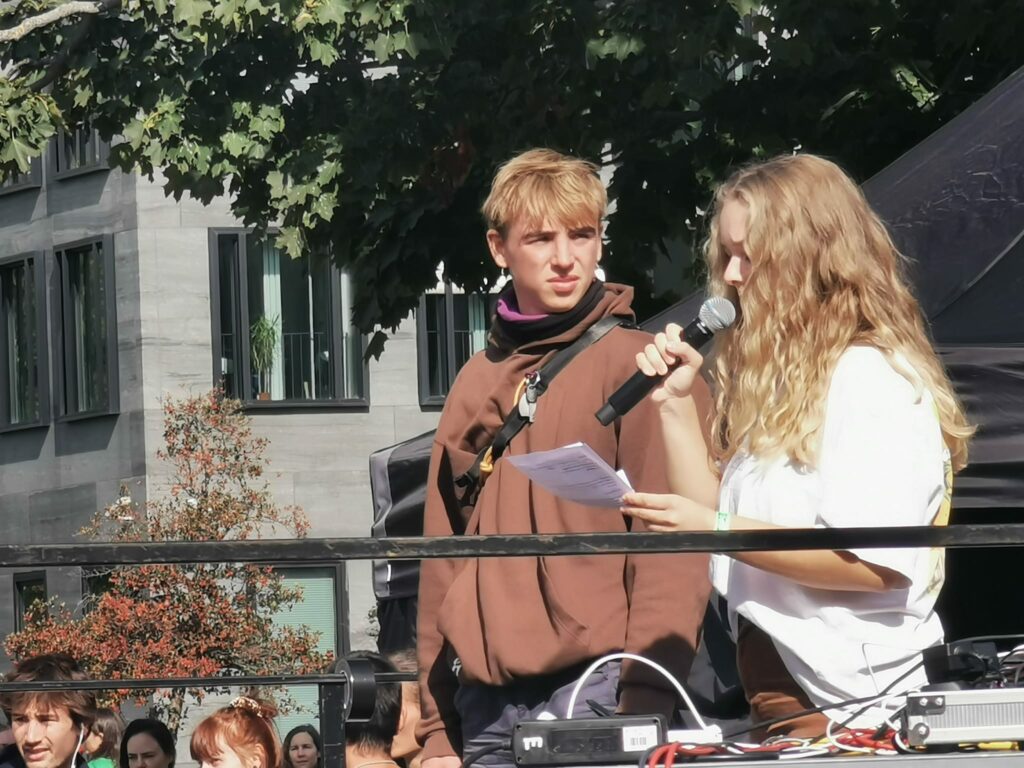
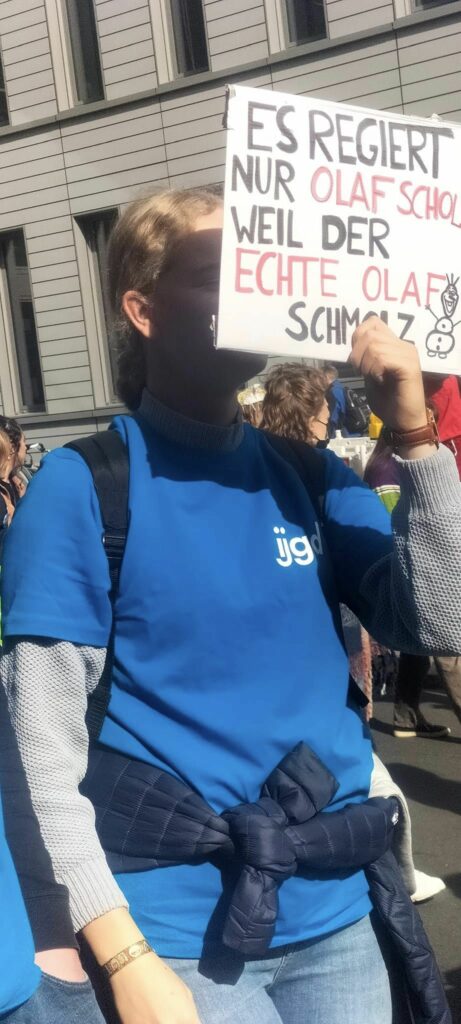
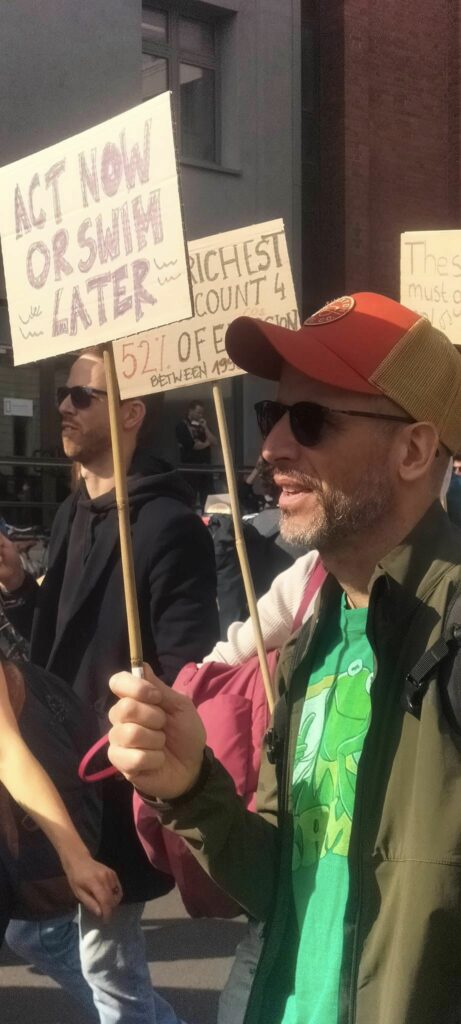
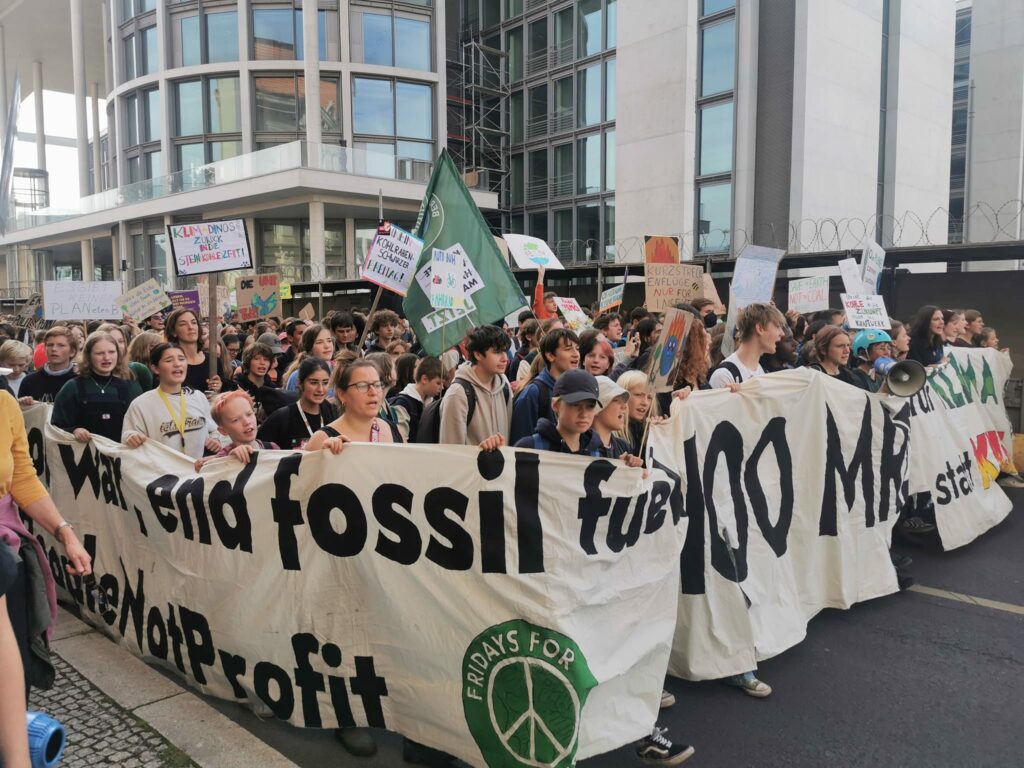
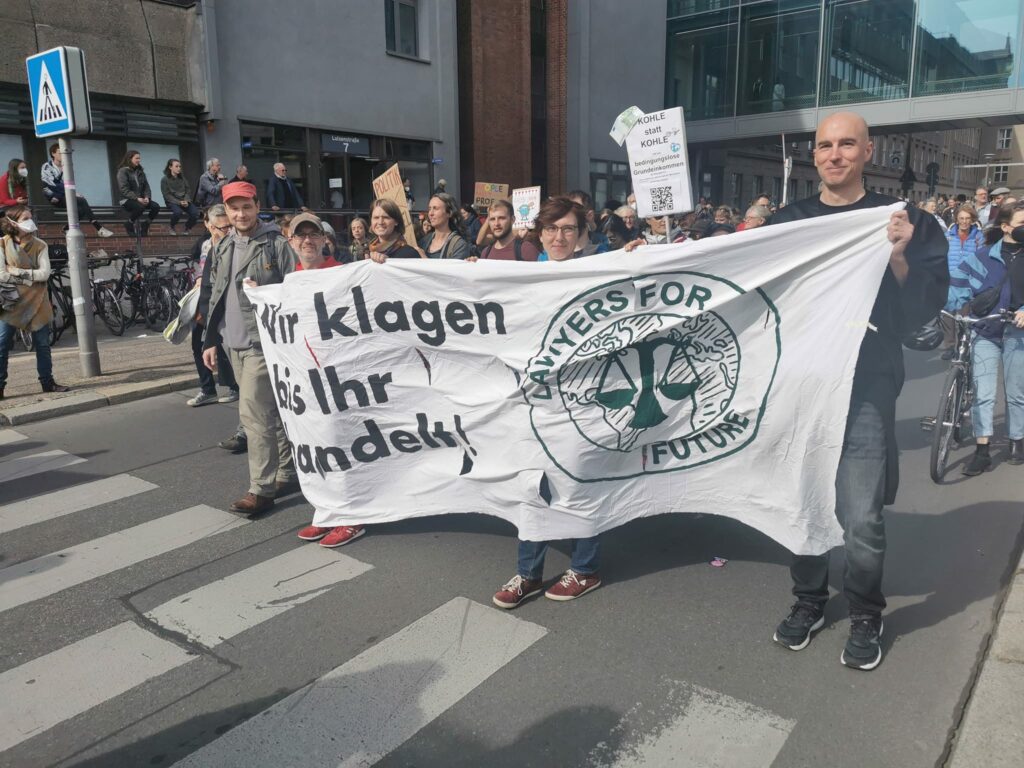
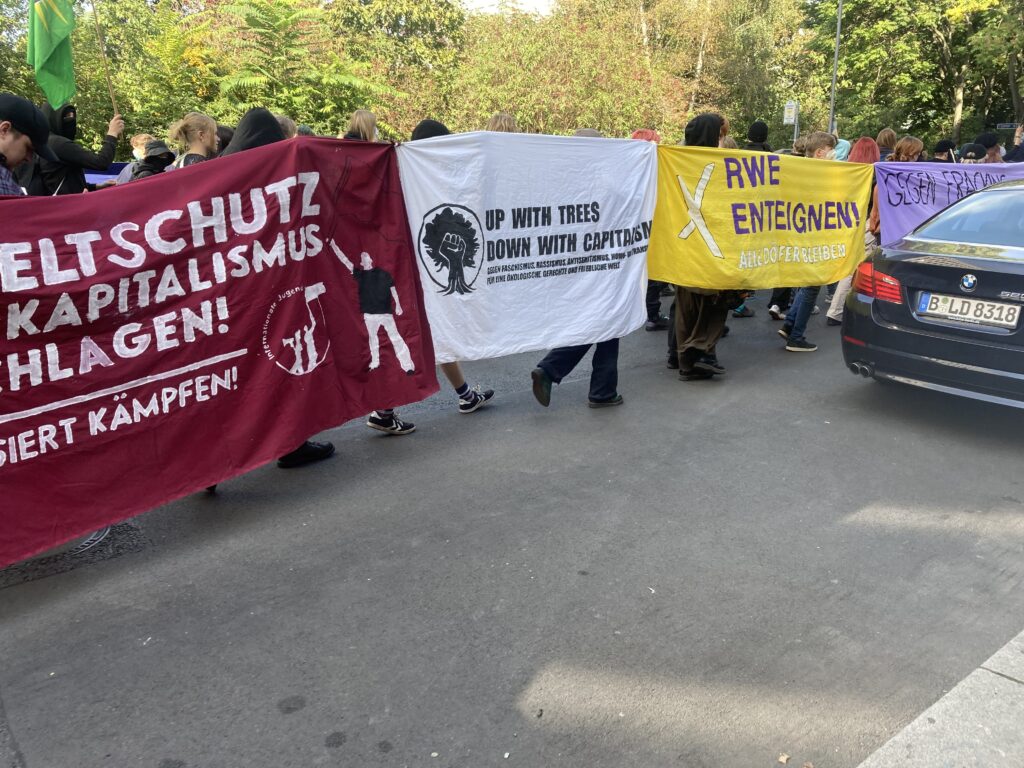
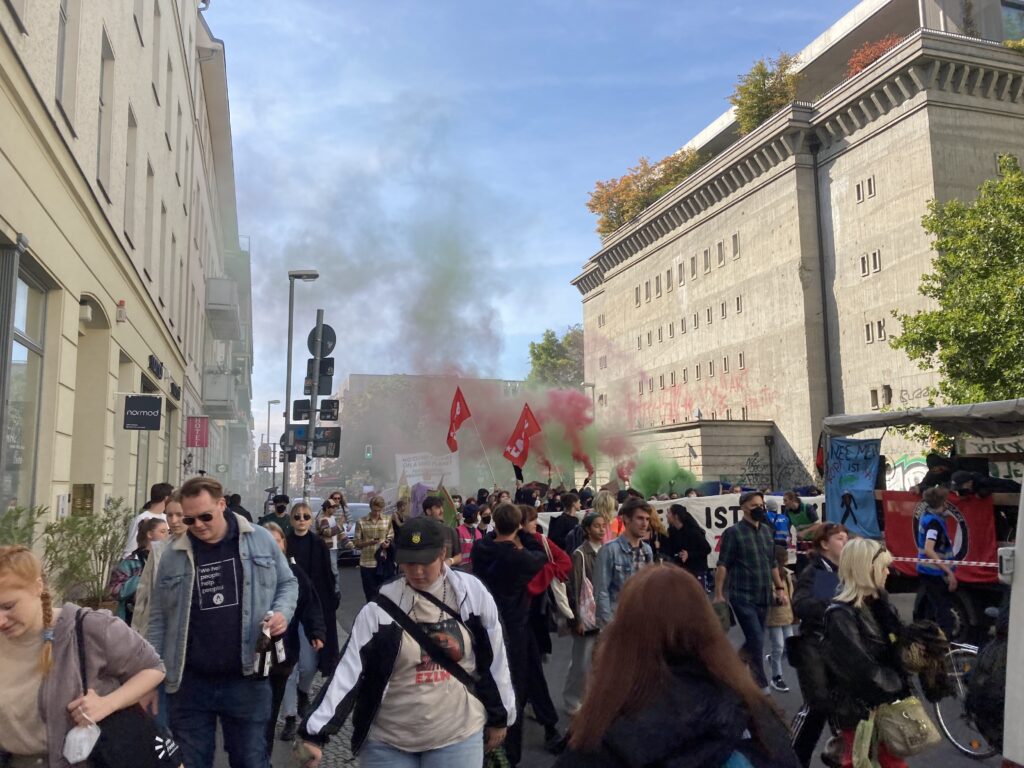
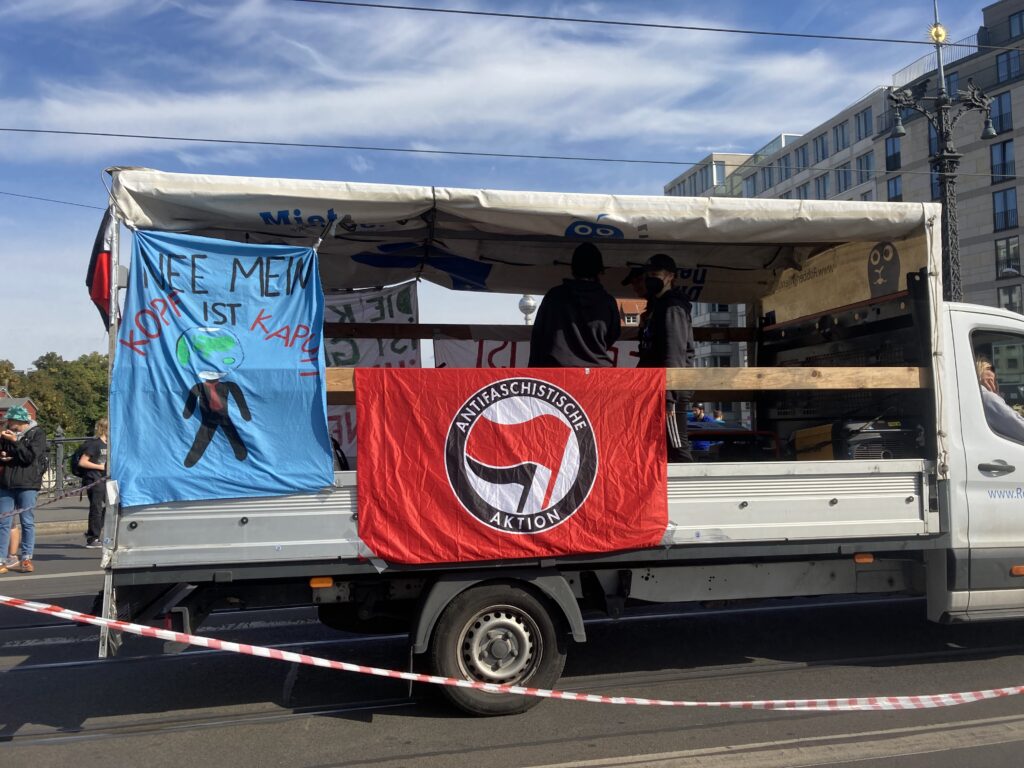
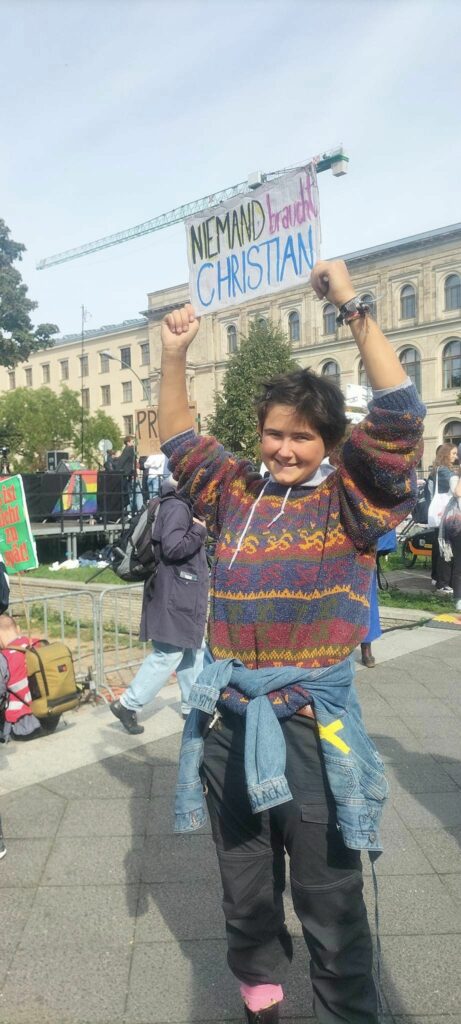





























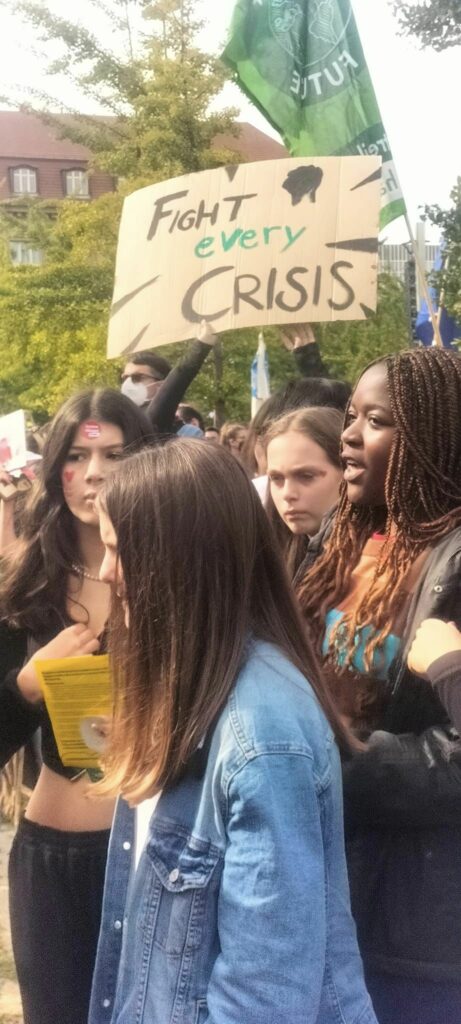







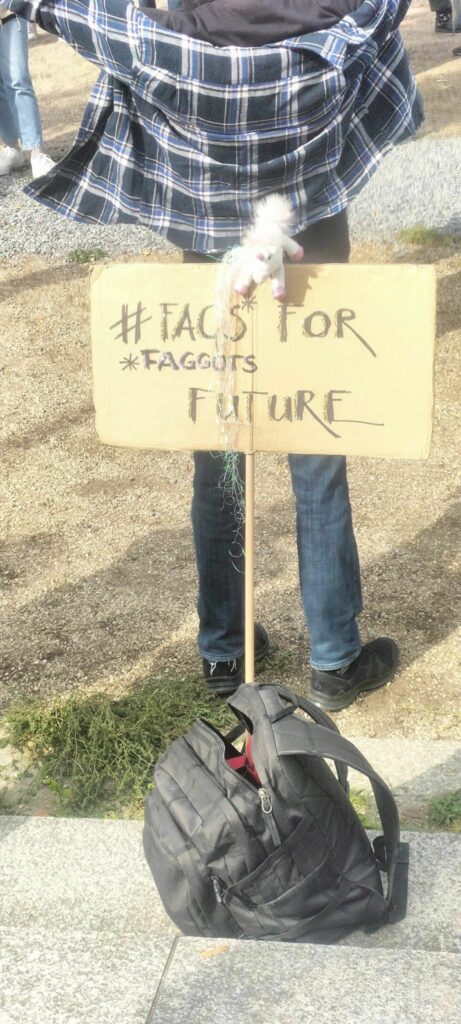



























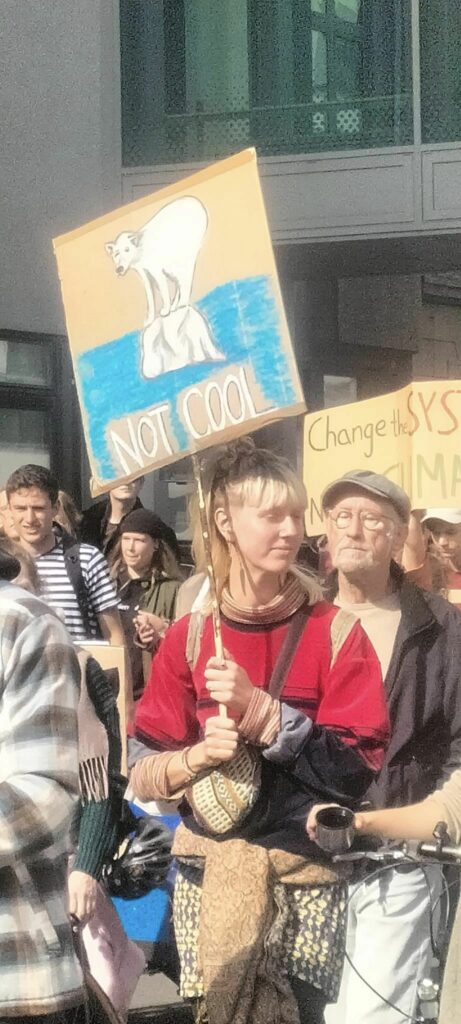










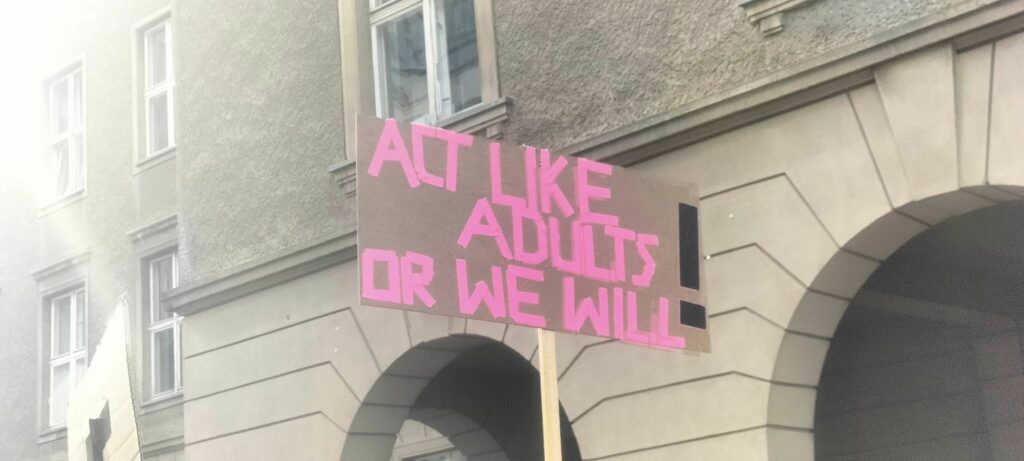




































Photo Gallery – Climate Strike Demo, 23rd September 2022, Berlin
Photos: Phil Butland, Dave Gilchrist. Rosemarie Nünning
The Left Berlin
24/09/2022

Photos: Phil Butland, Dave Gilchrist. Rosemarie Nünning
The Left Berlin
24/09/2022










































































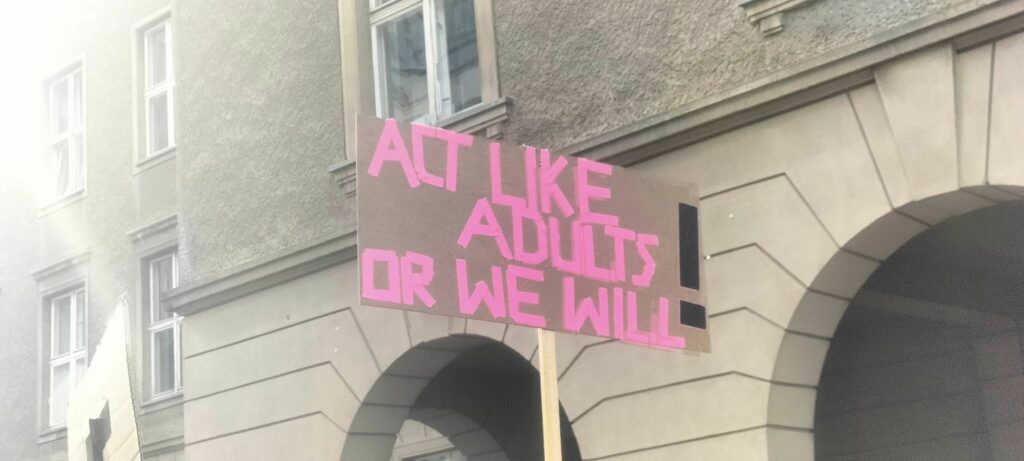

















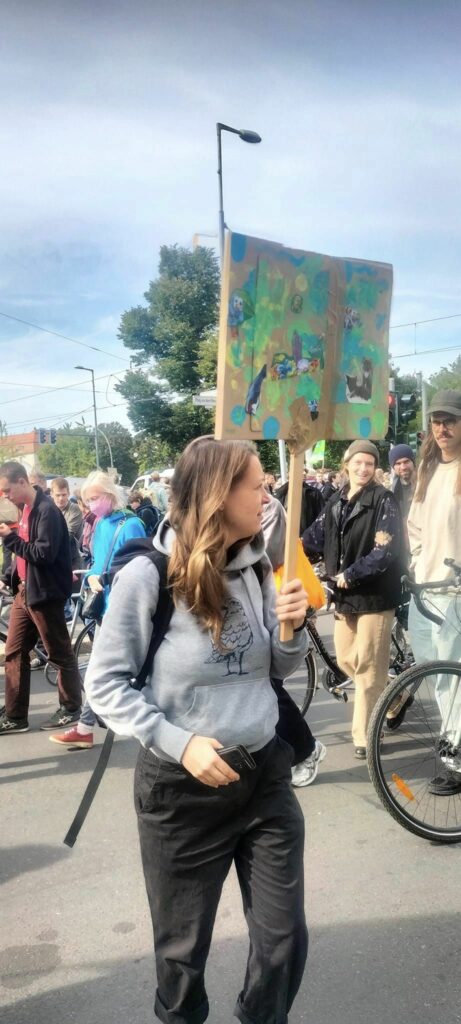



















The film maker, who died this week, was a product of his time, including the May 1968 movement
Dimitra Kyrillou
22/09/2022

Jean-Luc Godard’s death on September 13th had impact not only to cinephiles all over the world, but also to left-wingers, as his name is connected with both, radical cinema and political activism. So profound is the imprint he left, that after the emergence of his debut feature film “À bout de souffle (Breathless)” (1960), film theorists and historians have been talking about “cinema before” and “after” Godard.
Not everyone appreciates his cinematic work. While social network timelines have been flooded with photos of Godard films and praises over the “founder of modern cinema”, the “pope of Nouvelle Vague” or the last “iconoclast”, at the same time objectors describe films of boredom, elitism, insolence, incoherence, the latter being in a way implied by his own words: “A story should have a beginning, a middle and an end, but not necessarily in that order”.
This text stands basically in defense of Godard, the theorist, the filmmaker and the political being.
French New Wave
Godard was a pioneer, who walked upon challenging the course and the substance of cinema up to his time and sought to revolutionize it. He radicalized the visual and aesthetic of the film, turning cinematic rules upside down, inventing new notions and transforming tools: The “jump cut” – which until Godard’s innovations in “Breathless” was considered plainly an amateurish mistake – in his hands became a technique of deliberately eliminating segments of particular shots instead of removing the entire shot. Direct address to the camera, an element he introduced from Berthold Brecht’s epic theater, along with so called non-diegetic inserts (scenes coming from outside the made-up world of the film to be placed into the film). Breaking the fluid narrative that characterizes conventional cinema forces the viewers to take on more critical roles, connect the pieces by themselves, become participants in what is happening on the screen and, in distance from the protagonist’s struggle, get in the position to judge without sentimentality. Together with Francois Truffaut’s “The 400 blows” and Alain Resnais’s “Hiroshima mon amour” Godard initiated the French New Wave in cinema.
Nothing seemed to be the same anymore in the way of seeing and digesting a film. “Breathless” was the burst of this concept, but it continued throughout Godard’s so called first period, until 1968, with provocative and often controversial films, such as “The Little Soldier”, which was banned for years by the French authorities for addressing the Algerian War, “Masculine Feminine”, “Contempt”, “Pierrot le fou”, “Alphaville”, culminating with the “Weekend”, a virulent satire of the bourgeoisie, which premiered just before the events of May ’68 and actually introduced a new period, shaped by the rising of mass struggles in France (and worldwide). These films were diverse and radical, denouncing bourgeois values and authorities, the imperialist war in Vietnam, the consumer society (the children of Coca Cola) and their effect on human conscience.
Many critics argue that Godard simply ignored cinematic rules, because he was dogmatic and biased against Hollywood, or because he had not been trained in a proper film school. This is not the case.
Godard’s generation did not come out of the blue. Having worked on film theory around the magazine “Cahiers du cinema”, Jean-Luc Godard, François Truffaut, Jacques Rivette, Claude Chabrol, and Éric Rohmer, but also a circle including Alain Resnais, Agnes Varda, Chris Marker and others moved into directing as the “Nouvelle Vague” of cinema and engaged themselves into transforming art to a vehicle for change.
Far from being dismissive of American mainstream cinema, the group of Cahiers were film aficionados, who, before turning to directing had “devoured” hundreds of Hollywood movies and reflected and discussed the contribution of filmmakers such as Alfred Hitchcock, Howard Hawks and others to the making of cinema. Their transition to directing followed getting to know how cinema had worked before.
They challenged the notion of the cinema industry and the cinema moguls’ grip on the entire film production and juxtaposed the “auteur” theory, which emphasized the importance of the individual director, and the semi-mysterious concept of “mise-en-scène” (putting the scenes in order), essentially an attempt to analyze visual style. Of course, one would rightly argue that film-making is a collective process. But the criticism of the group of Cahiers referred to the big producers and to the market. At the end of the day, many of their films did, bear influence from the great Hollywood filmmakers and reference to genres.
Godard in May ‘68
Most of these people were actively involved in the May uprising, not just as filmmakers but also as activists of the revolutionary Left that emerged out of that period. The mood had already been heated by the dismissal of the founder of Cinémathèque française, Henri Langlois by the Minister of Culture Andre Malreaux three months earlier, and a defense committee had been created to support Langlois. These mobilizations were to be transferred to the Cannes film festival, which set off on May 10, 1968.
As demonstrations and strikes burst in Paris, Godard along with Truffaut and Claud Berri played a decisive role in delivering to the festival the calling of the general assembly of the people of cinema for the Cannes festival to be stopped, as a gesture of solidarity with the Parisian insurgents. Harsh political debate took place. In his famous address at the Cannes assembly Godard said “We are talking of solidarity with students and workers and you are talking dolly shots and close-ups!” It worked though. The jury and the artists were divided, and under the advance of the struggle in the rest of France, the festival was finally cancelled.
A few days later, a general assembly (États général) met in Paris and came up with a political manifesto for “cinema at the service of society and the revolution”. That was a formidable declaration, although its realization had to face practical and political obstacles. Soon, the assembly split into 19 different groups, each with its own concept of how to carry on the scope. Nevertheless, these initiatives were an original experiment for a cinema that would be determined not by dominant ideas and market laws, but by the creativity of its people and the needs of the movement. The main reason for this was of course the end of the mobilization and the return of France to “normality”, following an agreement between the trade union leadership and the political establishment.
Tziga-Vertov Group
Godard named the collective he created with Jean Pierre Gorin the “Tziga-Vertov Group” (DVG), a tribute to the Russian Revolution of 1917. He disavowed everything he had made up to that point as “capitalist” and declared that the collective “sought not just to make “political films” but to make films politically”. He was at the time identified as a devoted Maoist, which may seem grotesque today, however at that time Maoism was a dominant political current in the movement and stood critical to the French Communist Party which had capitulated to General De Gaulle’s maneuvers to end the revolt.
The films made by DVG are the most neglected of Godards, regarded strict and dogmatic by many, however they are challenging and, from a historic point of view a valuable documentation of the mood inside the working class and the movement during and in the aftermath of May ’68. For example, “A Film Like Any Other” is a non-narrative assemblage of filmed discussions between Renault workers and student activists intercut with footage filmed in the streets of France during the heated weeks of May 1968. “British Sounds” comments on the alienation of labour by involving quotes from The Communist Manifesto with striking car workers from Ford Dagenham and elsewhere. There is also a section on the then emerging women’s liberation movement. In the same spirit “Wind from The East” and “Struggle in Italy” attempt to speak on the politics bourgeois representation and the role of the left. “Vladimir and Rosa” is a parody of the Chicago 8 trial of the anti Vietnam War activists who were charged following protests at the 1968 Democratic Party convention. This was a clear attack on the criminalization of dissent and trial by media and the state. Godard would come back to these issues later.
This circle actually closed with fiction film “Tout va bien” (1972), where well-known actors Yves Montand and Jane Fonda were engaged to play a pair of middle-class intellectuals encountering a strike at a sausage factory. “Letter to Jane” was the epilogue to this film and the entire effort of the group, which dissolved soon after.
…and after
Godard went through a personal crisis, both physically (following a motor-cycle accident) and intellectually, and re-oriented himself and his activity. First in Grenoble, where he established his own studio and then to Switzerland. He took time to reflect on the retreat of the movement and the Left and came back with new stuff, dealing not overtly with class struggle, but with everyday life, relations, and sexuality, always retaining his political point of view. In the 1980s he produced films in a more refined artistical way, for which he received criticism from some of his earlier fans. More known are the melancholic “Prenom Carmen” (1983) and “Hail Mary”, which was condemned by the Catholic church as blasphemous. He declared once more his interest in cinema history with his 4.5-hour video project named “Histoire(s) du Cinéma” (1988–1998), denying the widespread notion of the 1990s that cinema was dead. On the contrary, his career would continue in the 21st century.
A supporter of Palestine
Godard remained during all his life committed to the Palestinian cause, defying the cost of being accused for anti-semitism. In the early days of the Tziga-Vertov Group, he and Gorin visited Jordan and spoke with Palestinian militants in order to prepare a documentary to be called “Till victory”. Tragically, most of those fighters were massacred by the Jordanian regime during the “Black September” of 1970 and the project was aborted, only temporarily, as Godard used the footage a few years later in his “Ici et ailleurs (Here and elsewhere)” film. In “Film Socialisme” (2010), he chose Palestine as one of his six “homelands” to visit in the last section of the film named “our humanities”.
In 2010, after the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences announced plans to award Godard an honorary Oscar, pro-Israel groups revolted, calling on the Academy to rescind the Oscar. Godard rejected the allegations by insisting that he was an “anti-Zionist”, not an anti-Semite, a fact that could easily be proved by the way he has depicted the holocaust in his documentaries. He did not hesitate to endorse cultural boycotts of Israel.
Legacy
“All you need to make a film is a girl and a gun” Godard once wrote, and proved it with “Breathless”. What he did not know is that with a girl and a gun he would change cinema. He transformed the way we see a film, what we expect from a film, and for that cinephiles owe him.
Godard followed with commitment the path of questioning and renewing his means of expression. The camera was for him a tool for artistic and political intervention. A Marxist and deeply politicized, he did not miss the opportunity, both with his films and with his life standing and his statements, to “disturb” all sorts of establishments in the artistic field and in society. Unapologetic, disobedient, stubborn, committed to the cause of socialism and communism, he never stopped seeing the world from the “left bank”.
Weekly news round-up from Berlin and Germany

NEWS FROM BERLIN
Union calls for all-day warning strike at Berlin’s schools
The Education and Science Union (GEW) has again called on its members in Berlin to go on warning strike on September 28. Teachers and school psychologists are to stay away from school all day. “The aim is to conclude a collective agreement on health protection, in which the ratio of pupils to teachers and thus the class size at general and vocational schools is bindingly regulated,” the union has announced. GEW also announced that it would extend its strike activities beyond 28 September and call for further strikes “in a timely manner”. Around 2,500 teachers participated in the last warning strike on 29 June. Source: tagesspiegel
Berlin pensioner pays almost 900 monthly euros for gas
Due to the energy crisis, many customers are seeing their gas bills rise significantly. This is also the case for Renate Sloma, an 82-year-old who suddenly must pay ten times as much as before. Yet she lives frugally, currently only turning on the heating briefly in the morning when she takes a shower. She gets her gas from Mitgas, which has given her an explanation, saying that the company believes that customers like Renate Sloma have long benefited from a favorable tariff with a fixed price guarantee. The new bill was “calculated at short notice”. In such cases, the consumer advice center suggests terminating the contract. Source: rbb
The €29 Berliner ticket
From October 1, Berlin will have the option to buy a monthly subscription for €29. But this ‘ticket’ has some differences than the popular 9-Euro-Ticket from last summer: it is actually a subscription and is valid only in the Berlin AB zone. Being a subscription, means you need to sign up for it on the website or app. And, quite importantly, that subscription does not end automatically on 31 December. This means you will have to cancel it before January or you will be charged for the month of January at the normal rate. Source: ExBerliner
NEWS FROM GERMANY
Active waiting
It is phenomenal what a communicative blunder the German government has made since the beginning of the war in Ukraine: it supports an attacked country with weapons – and yet it is seen at home and abroad as lacking solidarity and being useless. This is actually incorrect. The fact this support is not adequately realized is partly due to a distorted view of German Ukraine policy. To some extent, the German government can blame itself for the mistrust because of the hesitancy that precedes every new aid pledge, and which has long exceeded the level of justified caution. Source: taz
EU Commission launches infringement proceedings against Germany
According to the EU, national governments must ensure that there is enough time for family life alongside work. Germany has not communicated in time how the directive on the so-called work-life balance, which has been in force since 2 August, should be implemented at national level. Therefore, the EU Commission will send a letter of formal notice to Germany, as well to other 18 EU member states, initiating a so-called infringement procedure. The aim of the new directive is gender equality in labor market participation. The work-life balance directive also targets workers who care for relatives. Source: DW
Deutsche Bank expects a ‘longer and deeper’ recession in Europe
Last Wednesday, Deutsche Bank’s economists argued their previous prediction for a “mild recession” in Europe is no longer valid as the energy crisis has worsened substantially since July. Europe’s energy crisis has wreaked havoc on the global economy since the Ukraine war began, but its roots stretch back to years before the conflict. Even with alleviation measures, Deutsche Bank’s chief economist, Mark Wall, argues that the efforts won’t be enough to avoid economic disaster. Wall’s comments came just a day before Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered the “partial mobilization” of some 300,000 reserve troops in a major escalation of the war this week. Source: fortune
with Magda Qandil who has recently returned from the border between Poland and Belarus, Activists from Movimento dos Trabalhadores Rurais, and Emily Baumgartner and Phil Butland on the court victory of Farah Maraqa
In this episode, we’ll be hearing from:
This episode is presented by Ali Khan and produced by Tom Wills.
Please tell us what you think of the show by emailing radio@theleftberlin.com.
You can hear previous episodes of Radio Berlin International here.
Abortion: Our right, our choice! Here and worldwide!

This year, Section 219a of the German Penal Code (StGB) has finally been repealed, removing the ban on “advertising” abortions. Doctors will finally be allowed to provide information on all relevant aspects such as methods, procedures and costs of abortions and will no longer be subjected to pressure from opponents of reproductive rights, who used this absurd paragraph to criminalise doctors.
This long overdue step wouldn’t have been possible without significant pressure from the pro-choice movement, but we’re not ready to celebrate yet! As long as Section 218 of the German Penal Code exists, abortion is considered a criminal offence in Germany. We call on the federal government to act immediately and implement sexual and reproductive rights: because these are human rights!
We demand:
In 2022, sexual and reproductive rights are still not guaranteed in many countries around the world. On the contrary, they are under attack more than ever. In the USA, the right to abortion is currently under acute threat. In the neighbouring European country of Poland, abortion is de facto banned. As a result of these restrictive regulations, pregnant women have already died because doctors refused to perform vital abortions for fear of criminal consequences. People who fled the Ukraine war have also reported difficulties accessing abortions in Poland (even after rape).
Around the world we experience inequality and oppression as a result of constant attacks on sexual and reproductive health and rights. We stand in solidarity with all those fighting for reproductive justice and demand unrestricted physical, sexual and reproductive self-determination for all, especially women, non-binary and trans* people, and people with disabilities – in Germany and worldwide!
Berlin action: 6pm at the Haus der Statistik, Otto-Braun-Straße 70-72, Wednesday 28th September